
Your credit score is more than just a number — it is the key to unlocking financial opportunities. Whether you are aiming to qualify for a mortgage, secure a low-interest loan, or get approved for a top-tier rewards credit card, a good credit score can make all the difference. It impacts not only your ability to borrow but also the cost of borrowing. If you are wondering what qualifies as a “good” credit score and why it matters, understanding this can help you take control of your financial future.
What Is A Good Credit Score
Your credit score is a three-digit number that reflects your creditworthiness — essentially, how likely you are to repay debts. Credit scores typically range from 300 to 850, with different lenders and institutions using various scoring models, the most popular being FICO and VantageScore. A good credit score can open the doors to better financial opportunities, like lower interest rates and access to premium credit cards.
Credit Score Classifications
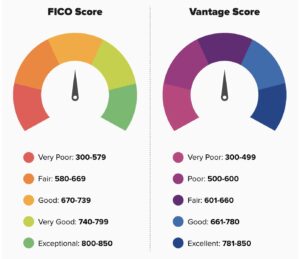
Credit. Experian. FICO vs VantageScore Credit Ratings.
Credit scores are typically broken down into categories that lenders use to evaluate your financial risk. Here is a closer look at how FICO scores are classified:
- Exceptional (800-850): Those with scores in this range are considered the most creditworthy. They usually enjoy the lowest interest rates and the best credit card and loan offers.
- Very Good (740-799): A very good score qualifies you for favorable terms on financial products, though maybe not as excellent as those with exceptional scores.
- Good (670-739): This range is generally considered solid by most lenders. You will likely be approved for credit, though you might not always get the best interest rates.
- Fair (580-669): Fair credit suggests higher financial risk, so lenders may offer credit with higher interest rates or stricter terms.
- Poor (300-579): Poor credit makes it difficult to qualify for most forms of credit, and if you do get approved, expect steep interest rates and limited product offerings.
What Is The Highest Possible Credit Score
The highest possible credit score is 850. While obtaining a perfect 850 is rare, having a score above 800 already puts you in an excellent position to qualify for the best interest rates and credit products. It is important to note that once you reach the “exceptional” range, the benefits of having a higher score become marginal — meaning there is no need to obsess over hitting a perfect score.
What Determines Your Credit Score

Credit. Experian. What Factors Determines Your Credit Score.
Several factors work together to determine your credit score. Each factor is weighted differently, so it is essential to understand how these elements interact to shape your score. By focusing on these areas, you can improve your score over time.
Payment History (35%)
The most critical component of your credit score is your payment history, which accounts for 35% of your overall score. Lenders want to know if you consistently pay your bills on time, as this is a good predictor of how you’ll handle future credit obligations.
- Impact Of Late Payments: Missing a payment, or paying late, can significantly damage your score. For example, a single missed payment can cause your score to drop by as much as 100 points if it’s reported 30 days late or more.
- Avoiding Damage: To avoid penalties, set up automatic payments or calendar reminders so you do not miss due dates. Even one late payment can stay on your report for up to seven years, though its impact diminishes over time.
Outstanding Balances Or Credit Utilization (30%)
This factor looks at how much credit you are using compared to how much you have available. It is often referred to as your credit utilization ratio, and it makes up 30% of your score.
- Credit Utilization Ratio: Ideally, you want to use less than 30% of your available credit. For instance, if you have a credit card with a $10,000 limit, keeping your balance under $3,000 can positively influence your score. Lenders view high utilization as a sign you may be over-reliant on credit.
- Reducing Utilization: Paying down your balances and avoiding maxing out your credit cards can help. Even small steps, like making multiple payments throughout the month, can keep your utilization ratio low.
Length Of Credit History (15%)
Your length of credit history refers to the age of your oldest credit account, the average age of all your accounts, and the length of time since you last used those accounts. This accounts for 15% of your score.
- Why It Matters: A longer credit history gives lenders more information about how you have managed credit over time. The older your accounts, the better it reflects on your ability to handle long-term financial responsibilities.
- Keeping Older Accounts Open: Even if you no longer use certain credit cards, keeping older accounts open can benefit your credit score by contributing to the average age of your accounts.
Note: Some issuers of credit cards shut down (i.e. close) accounts with no activity within a certain period of time. In order to avoid this, and keep your oldest account open, make sure you use any active credit card at least once per year.
New Lines Of Credit Or Hard Inquiries (10%)
Opening several new credit accounts in a short period can signal risk to lenders, which can temporarily lower your score. Each time you apply for new credit, a hard inquiry is made, which may decrease your score by a few points. This category makes up 10% of your credit score.
- Avoid Over-Applying: While applying for new credit is not always a bad thing, multiple applications in a short time can cause concern. It is wise to space out new credit applications and only apply when necessary.
Credit Mix (10%)
Your credit mix refers to the different types of credit you have, such as credit cards, auto loans, mortgages, and personal loans. This makes up 10% of your score.
- Why It Helps: Lenders like to see that you can manage various forms of credit. A diverse credit mix shows that you are responsible across multiple types of credit products.
- Do Not Open Accounts Just For Variety: If you do not have a mortgage or auto loan, it is okay! While having a mix helps, it is not necessary to open new accounts just for the sake of diversity.
How To Check Your Credit Score

Credit. USA Today. How To Check Your Credit Score.
It is important to monitor your credit score regularly to stay on top of changes and catch any errors on your credit report. Here are a few ways you can check your credit score:
- Credit Monitoring Services: Websites like Credit Karma, Credit Sesame, and Experian offer free access to your credit score and credit monitoring tools. While they might not always show your FICO score, they can give you a good idea of where you stand.
- Your Credit Card Provider: Many credit card issuers now provide free access to your credit score as a benefit. Check your account dashboard or app to see if this feature is available.
- AnnualCreditReport.com: This government-approved site allows you to get a free credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) once a year. While your report will not include a score, it gives you detailed information about your credit history, which you can use to assess your credit health.
Credit Card Recommendations Based On Your Credit Score

Credit. Lending Loop. Your Credit Score Determines Credit Card Eligibility.
Your credit score not only determines your ability to get approved for credit cards but also influences the kinds of cards available to you. Here is a breakdown of credit card recommendations based on credit score ranges:
Very Good To Exceptional Credit Scores (740 – 850)
If your credit score is in this range, you have access to a wide variety of credit cards, including rewards cards, travel cards, and cash back cards. Look for options that offer sign-up bonuses and long-term value through card perks and benefits. Here are a few card options:
- Capital One Venture X Rewards Credit Card
- The Platinum Card® from American Express
- Chase Sapphire Reserve®
Related: The Best Luxury And Premium Travel Credit Cards
Good Credit Score (670 – 739)
For those with good credit, you still have access to a wide variety of credit cards including travel rewards cards, travel cards, and cash back cards. However, the focus is still on improving credit – especially if your score is below 700 – and responsible financial management. Here are a few card options:
- Capital One Venture Rewards Credit Card
- Chase Sapphire Preferred® Card
- Citi Premier® Card
Related: The Best Travel Credit Cards For Beginners
Poor To Fair Credit Score (Below 669)
If your credit is below 669, it is crucial to start improving or rebuilding your credit with secured credit cards. These cards require a cash deposit, but with responsible use, they can help you rebuild your credit and qualify for better products in the future. Here are a few cards to help you rebuild your credit:
- Capital One Platinum Secured Credit Card
- Capital One Quicksilver Secured Cash Rewards Credit Card
Final Thoughts
A good credit score is an invaluable financial tool that can unlock better interest rates, higher credit limits, and access to premium credit cards. Generally, a score between 670 and 739 is considered “good,” but striving for a higher score will open up even more financial opportunities. By focusing on improving key factors like payment history, credit utilization, and the length of your credit history, you can boost your score over time. Regularly checking your credit and making informed financial decisions will help ensure you maintain a healthy credit score, allowing you to reap the benefits of financial flexibility.